Growing with hydroponics turns any basement, warehouse, shipping container or greenhouse into a high productivity fruit and vegetable garden. Without the need for sunlight, soil or a large plot of land, hydroponic systems give you total control over the plants, nutrients, and quality of the food you eat. There has never been a better way to eat local!
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants in water. It replaces soil with a mineral solution of Nitrogen, Calcium, Iron, magnesium and other micro-nutrients directly to the roots for fast and healthy growth. This direct method of feeding allows them to focus their energy on growing strong stalks and higher yields rather than searching through the soil for nutrients.
Using this method of growing plants, farming can be done nearly anywhere on earth and even in space. The recent advancements in grow light technology have given hydroponics mass adoption but the idea of growing plants without soil has been around since the 1600s. In this article, we will take an expanded look at what makes Hydroponics the farming method of the future.

The Most Common Hydroponic Systems
There are a few common hydroponic system designs used by growers that differ in size and complexity. Variations on each system have been developed by commercial growers and hobbyists trying to find the most efficient methods of food production.
Ebb and Flow Hydroponic System
The Ebb and Flow system is based on an elevated flooding table concept. The plants grow in a large tray with their roots covered by stone. The entire tray is periodically flooded with a nutrient solution and then allowed to drain away back into the reservoir until the next flooding cycle begins.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Hydroponics
The Nutrient Film Technique is commonly done using a covered trough with holes cut out on top for the plants stalks to grow upward. The trough is designed with a gentile slope allowing gravity to move a thin film of nutrient solution from one end to the other.
As the nutrient film works its way down the trough, it flows over the plant roots providing them with the nutrients they require for healthy growth. The low end of the trough empties back into the reservoir to be recycled back through the system.

Deep Water Culture (DWC) Hydroponics
Deep Water Culture systems keep the plant roots submerged in a nutrient solution at all times. Simple systems use a series of buckets or tubs as a grow chamber and water reservoir in one. The plants grow out of a net cup located above with the roots extending down into the reservoir.
This is the safest and simplest method of hydroponic growing because a loss of electricity won’t leave the roots exposed to dry out. DWC systems use an air stone at the bottom of the reservoir to keep the nutrient solution oxygenated so the plants don’t suffocate and die.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics is a hydroponic variant that keeps the plant roots suspended in an air chamber rather than in water. The nutrient solution is delivered as a mist making it easier for the roots to absorb and keeps the grow chamber at a high humidity level.
The excess supply of oxygen around the roots in an aeroponic system increases the efficiency of nutrient uptake while water usage in the system is reduced by over 90%.
The Tower Garden Vertical Aeroponic system is my favorite way to grow food at home. The simple and efficient design lets me grow 28 plants in a 3′ by 3′ space. It’s incredibly easy to operate because the automatic timer does all the work, I just top up the reservoir and eat the food within steps of my kitchen.
You can read more about this Ready-To-Grow system in my complete guide to the Tower Garden.
What is Vertical Hydroponics?
Hydroponic systems can be easily adapted to a vertical farming setup for more production in a smaller footprint. Many commercial operations use a stacked tray method of growing greens and other smaller plants with the use of shelving and LED light strips.
The standing vertical garden uses a central watering system that feeds plants growing outward from around a center column. This style of vertical gardening provides the most efficient use of space and is easier to access, inspect and harvest the plants.
How Does Hydroponic Farming Work?
Plants require a few basic things in order to grow. They need light, air, nutrients, space, and water. Without all of these, it just doesn’t work. But, you’ll notice the one thing missing from the list is soil.
Soil holds moisture, supports the root structure and is filled with minerals and micro-nutrients essential in plant growth, unfortunately these basic factors get depleted as they’re consumed by the plants.
In a Hydroponic system, the nutrient solution is continually replenished in the reservoir. This ensures the plants are never starved of the essential nutrients they need to grow and produce nutritious yields.
The use of a grow medium helps keep the plant upright while also shielding the roots from direct sunlight and drying out. Hydroponics takes the mystery out of feeding your plants, you have direct and total control over the inputs to your garden.

Components of a Hydroponic System
Growing plants in soil is definitely more straightforward. Without ever having grown a plant, a person could grow something from a seed in the soil fairly easily with a little trial and error. A hydroponic system has more moving parts that all need to be in the right place.
Grow Trays
Grow trays come in different forms including pools, long pipe, or even a bucket or simple food grade container. The trays contain the roots of the plant and provide a way for the nutrient solution to be supplied directly to them as needed.
Nutrient Solution
A good quality mineral blend comes in 2 or more concentrated formulas that get added to the reservoir water separately and mixed together. This prevents the minerals from binding, keeping them small and easy for the roots to absorb.
It’s important to keep the water away from direct sunlight to inhibit the growth of algae and molds that could kill the plants. Oxygenation of the water can be done using an airstone or creating agitation by allowing the water to fall back into the reservoir creating bubbles.
- Packaging Update: You may receive previous or updated packaging during our transition. Same...
- Simplify Your Feeding Routine: Our easy two-part system requires no complex schedules or...
- Compatible With Any Grow Setup: Humboldts Secret nutrients are built for results in deep water...
Nutrient Reservoir
The reservoir contains the mix of dissolved minerals and micro-nutrients typically found in soil with freshwater used to feed the plants. The reservoir can be part of the growing chamber as in a DWC system or separate as with an ebb and flow system.
Water Delivery System
The water delivery system uses pumps to provide the much needed nutrient solution from the reservoir to plants. Many system designs work on a timer at specific intervals and consist of small irrigation tubing or larger poly pipe.
Growing Medium
Without soil, plants in a hydroponic system still need something to grow in. Their roots need something that can hold the weight of the plant and support the root structure as it absorbs water and nutrients.
A growing medium is typically pH neutral, so balancing the nutrients in the system is easier than if we were to plant in soil. They are also porous so the roots can spread out and expand with the plant. Common substrates are rockwool, clay aggregate, coconut chips, vermiculite, peat moss, different kinds of rock, and even sand.
LED Grow Lights
Advances in LED grow light technology have substantially reduced the cost of starting and operating a hydroponic system. LED’s consume much less power and deliver full spectrum light to enhance the growth and flowering phases of your plants.
- Please note that we have a brand new upgrade.This product is compatible with Barrina GM Series...
- Full Spectrum: Barrina LED grow lights 4ft provide indoor plants with full-spectrum sunlight...
- Super Bright and High PPFD: Consuming only 252W with 1152 LEDS totally, replace 1400w general...
Indoor Space To Grow
The best place to grow hydroponically is indoors. This could be in a spare closet, an unused bedroom, a converted shipping container, or a greenhouse.
Growing indoors eliminates many of the outdoor problems such as pests, disease, and inclement weather. Grow tents help create a dedicated space to grow you plants. It’s much easier to control the environment of a smaller space and closing the doors helps reflect and improve the efficiency of your lighting system.
These are the most basic parts of a system and all you should require to get started. As long as the five basic needs are met, your hydroponic system should be able to churn out veggies at a surprising rate. For different types of plants, it may be necessary to introduce additional supplements and nutrients to a system.
The Benefits of Hydroponic Gardening
With hydroponics the advantages far outweigh the disadvantages, which is why hydroponic farming is seeing an upward trend, and most likely will continue to, as humanity grows and expands. Even into space.
Grow Food Anywhere With Hydroponics
Underwater, in the desert, on the roof of a skyscraper, in outer space. You read that correctly. There is a reason that NASA looks to hydroponic farming as the method we will use to feed astronauts and colonists on Mars in the not-so-distant future.
As long as you have the simple requirements that plants need to grow, you can design a hydroponic system that will work wherever you need it to. Not only can you grow anywhere, but you can grow more in less space when compared to traditional farming in soil.
Hydroponic systems can take advantage of height and can be stacked one on top of another to create vertical farms. Try doing that with corn planted in the dirt.
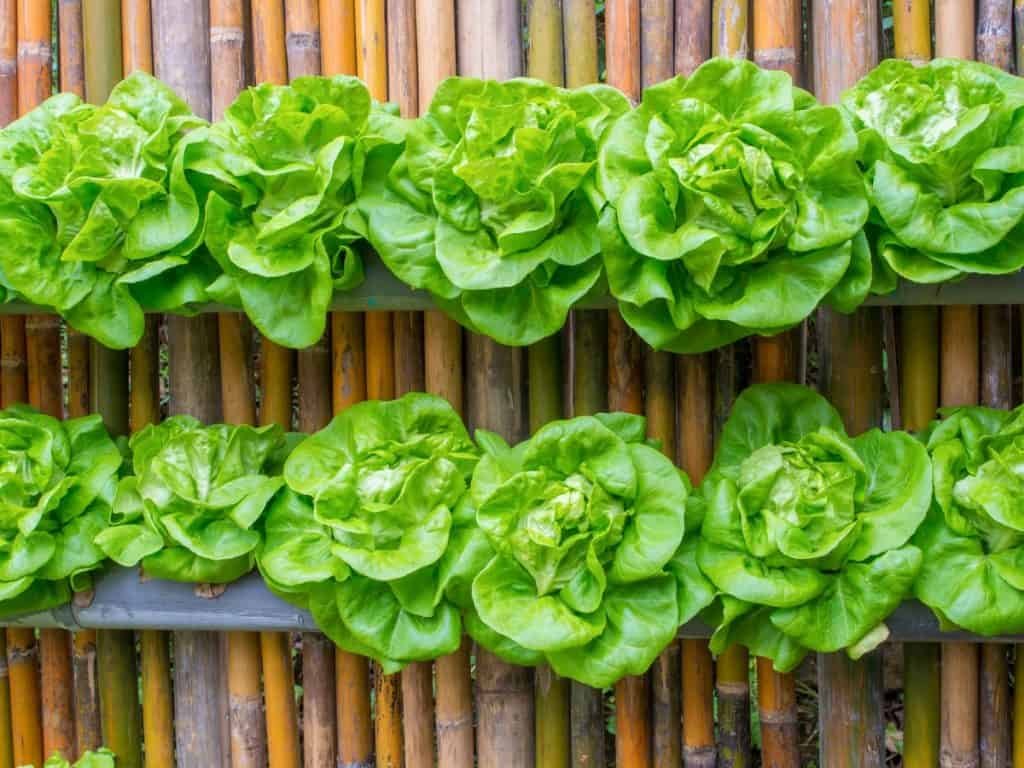

Hydroponic Systems Use Less Resources
Space, electricity, and most importantly, water. It might seem that because “hydro” is in the name and since the system relies so heavily on water, that it means that a lot of water might go to waste. It’s actually the opposite.
A hydroponic system uses only a tenth of the water that would be used on crops of the same type and size if they were grown in soil. When farming in soil, a lot of water is lost when it is absorbed by the soil and it is wasted in large scale sprinkler systems due to evaporation.
With the closed system of a hydroponic farm, very little is lost. This is immensely beneficial for places with poor access to water, or even during droughts. And let us not forget that it makes it quite possible to grow plants in space. It might not surprise you to learn that there isn’t much accessible water in space.
Plants Yield More Food And Grow Faster
It almost seems too good to be true. When you take out all of the struggles in life that a plant faces when it is grown outdoors, in the soil, they tend to do very well. Nutrients, water, and oxygen are delivered straight to the root system. It’s almost as if the plants are being spoon-fed as they lounge around all day.
This combined with the fact that the plants don’t have to allocate energy to warding off pests, regrowing damaged structure, or seeking food and water, they can focus the entirety of their being on growing. Without the constant struggle for survival, plants grown in this fashion shoot up like…well, weeds.
Not only will plants grow faster, but the edible parts of the plants also grow larger. It is easier to feed more people with fewer resources. Yet another reason why hydroponics is the future of farming.
Problems Are Easier To Troubleshoot
When the system is enclosed, it is protected from a lot of what causes problems in traditional methods of farming. This makes it easier to figure out what the problem is. The person in charge of the operation sets the parameters of the garden.
It is super easy to know what nutrients are in the water because you put them there. Since there isn’t any outside interference it is easy to see what variable is affecting what. It is doubly easy to keep a system in homeostasis as you can measure the nutrients, the pH, and easily replicate those amounts. Consistency is king with hydroponics and the system itself makes that easier to maintain.
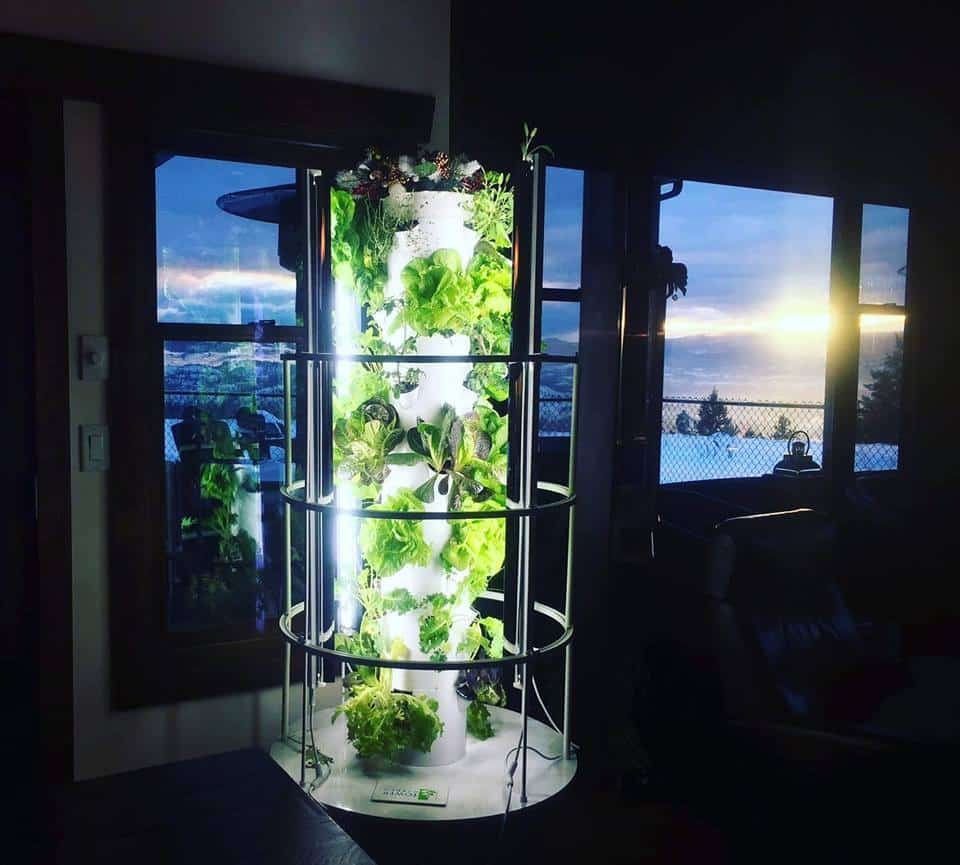

Hydroponic Gardening Requires Less Physical Labor
There is no stooping over the dirt to pull weeds and check for pests. Nor is there the need to work under the blistering sun or against a driving wind filled with pollen and wasps. Once a system is running, most of the work is done automatically. You plant the plants in their growth trays, in their medium, switch on the water delivery system, fill the nutrient reservoir, and boom, your job is done. Until harvest time that is.
Even then, the work is lessened to a high degree. The vegetables can be easily accessed and there is no dirt to wash away. Then when you’ve reaped what you sowed, you start over again and watch the system do the work for you once again. There is no tilling soil, or plowing or lugging water and fertilizer around all day. Only the beautiful system in motion.
No Soil Means Cleaner Production
One of the most simple benefits of growing vegetables without dirt is that your vegetables remain clean. As long as a hydroponic system is well monitored, maintained, and cleaned, the vegetables grown within the system will never have touched dirt in their lives.
In a perfect hydroponic operation, you wouldn’t even have to wash the vegetables after harvest. You could eat them straight off the grow tray if you so choose. And because there are fewer pests without soil, there are no harmful insecticides to rinse off.
Fertilizers and other chemicals used to treat disease and pests can run off into neighboring rivers and lakes and even sink down into the aquifer deep below the surface. With a hydroponic system, there is no need to constantly refresh the dirt’s mineral content and there is virtually no waste from the system. Just clean, delicious fruit and vegetables.
A Brief History Of Hydroponics
Francis Bacon wrote about growing plants without soil in 1627. It has only been improved upon since then.
After Francis Bacon began to ponder the concept of growing plants without soil, mankind’s interest in the idea continued to grow. In 1699, John Woodward, an English naturalist experimented with growing spearmint hydroponically. He discovered that when he used less-than-pure water, as opposed to pure, distilled water, the spearmint grew faster and larger, thereby hypothesizing that the nutrients present in the water aided in the plant’s vitality.
In 1929, he grew tomato plants in his back yard that stretched upwards twenty-five feet. He grew them in a nutrient-rich solution instead of soil and dubbed the process, aquaculture. Later on, he realized that the term aquaculture was already in use as the study of aquatic organisms and soon after changed the name to hydroponics, or water culture.
Throughout the early 1900s hydroponics saw use on more and more fronts. In the 30s, on Wake Island, an atoll in the Pacific used as an airline refueling station, Pan American Airlines grew fresh vegetables using hydroponics in order to feed passengers. This is one of the earliest, successful uses of hydroponics for farming. By 1982, hydroponics was on display at Walt Disney World’s Epcot Center at the Land Pavilion section of Future World.
By 2007, a company in Willcox, Arizona called Eurofresh Farms sold over 200 million pounds of hydroponically grown tomatoes. Hydroponics took a while to get its momentum going, but once it hit the twenty-first century, it was going at full steam.
It is estimated that the hydroponics market will have tripled by 2023 as more global economies grow and the demand for produce stretches with them, more and more resourceful economies turn towards hydroponics as a source for produce.
In Conclusion
Hydroponic growing gives us the opportunity to take total control over the inputs and environment of our food supply. Any sized space can be made into a product food growing area whether its in your home, garage or greenhouse.
Small systems are easy to build at home and buying a ready to grow system can get you started growing right away.
Don’t let fear of the unknown hold you back, start taking control of your food supply today and get the benefits of local, delicious and nutritious food at home.


